- The USD/CLP is rebounding, gaining 1.39% in today’s session.
- Copper increases losses and signs third consecutive session on the decline.
- Chilean President Gabriel Boric promotes his country’s economic and financial conditions during his visit to Paraguay.
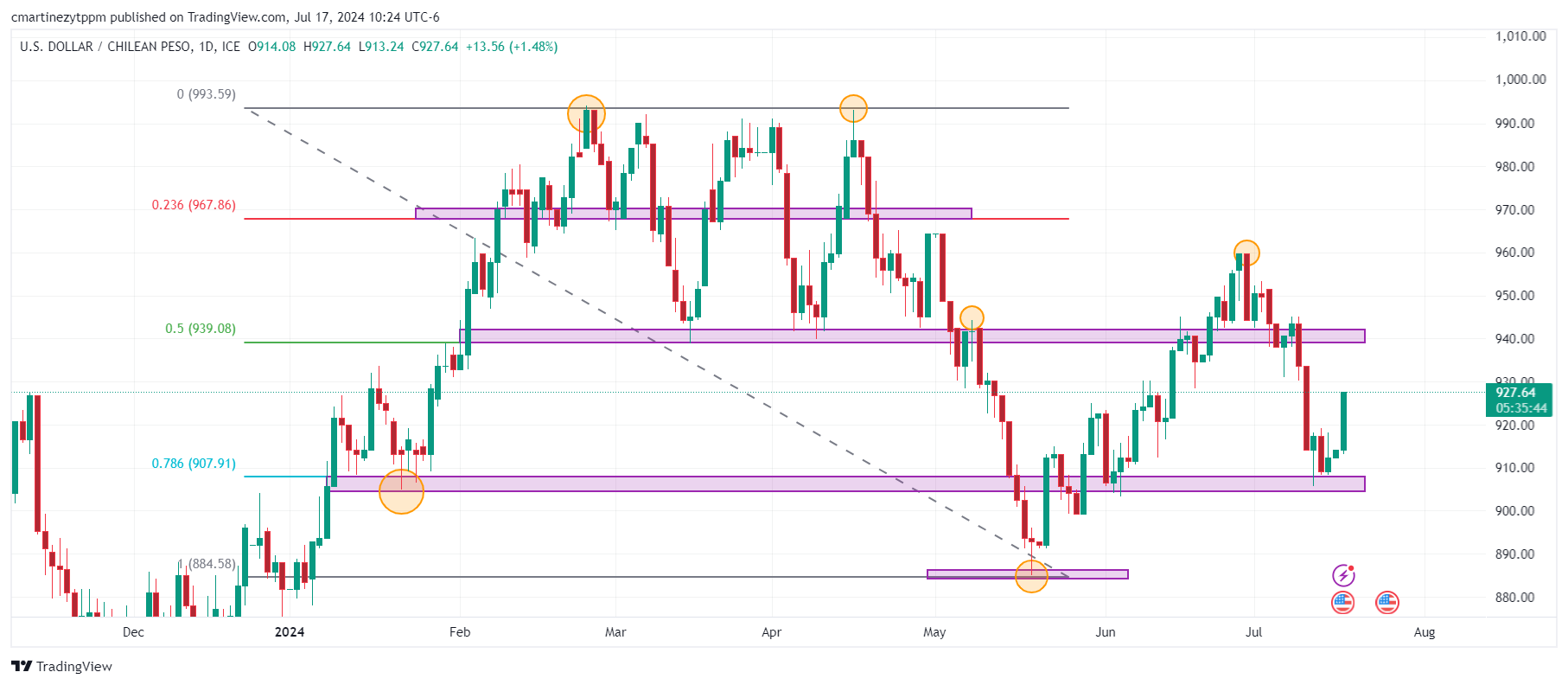
The USD/CLP marked a session low at 913.24, finding buyers who pushed the pair to a daily high of 927.64. Currently, the US Dollar price against the Chilean Peso is trading at 925.93, gaining 1.30% on the day.
Chilean peso weakens as copper erases July gains
USD/CLP has soared to five-day highs, setting a three-session winning streak. Copper, on the other hand, is trading at $4.39, losing 1.02% on the day. The metal is looking to consolidate its second consecutive week on the downside, approaching the 4.31 support.
Chilean President Gabriel Boric took the opportunity to promote the bioceanic corridor during his visit to Paraguay. The president highlighted the recovery of the Chilean economy and the expansion of industries focused on lithium and green hydrogen aimed at combating climate change.
Technical levels in the USD/CLP
The USD/CLP has reacted to the upside at a first support located in the 907-905 zone which converges with the 78.6% Fibonacci retracement. The next support is located at 885.00, the low of May 20. The closest resistance is located at 940.00, the high of July 8 which converges with the 50% Fibonacci retracement.
Chilean Peso Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The United States Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the de facto currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation alongside local banknotes. As of 2022, it is the most traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange transactions, equivalent to an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day. Following World War II, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency.
The single most important factor influencing the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and to promote full employment. Its main tool for achieving these two goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed raises rates, which helps the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a jammed financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks are not lending to each other (for fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy US government bonds, primarily from financial institutions. QE typically leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal of maturing securities in new purchases. It is generally positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







